Intraday trading is a popular way of making money in the stock market. It involves buying and selling shares within the same trading day, with the aim of profiting from small price movements. However, many traders are not aware of the tax implications of intraday trading income.
The first step in understanding the tax implications of intraday trading is to identify whether you are a trader or an investor. This distinction is crucial because it determines how your income from shares is taxed.
Investors benefit from lower tax rates on capital gains, while traders have the advantage of claiming business expenses that reduce their income.
If you are identified as a trader, your income from trading is treated as business income and is taxed under the head “Profits and gains from business or profession.” Your profits are taxed as per the applicable slab rates, which can go up to 30% depending on your income level.
Tax Calculation For Intraday Trading
Intraday trading income is considered speculative business income because you are trading without intending to take delivery (ownership) of the contract. As such, you must file ITR-3 and prepare financial statements. A tax audit may be applicable depending on your profit, loss, and turnover.
According to the Income Tax Act, intraday trading income is treated as “speculative business income" and taxed at the normal rates applicable to your income slab. This means that you have to pay tax on your intraday profits irrespective of whether you hold them for a short or long duration.
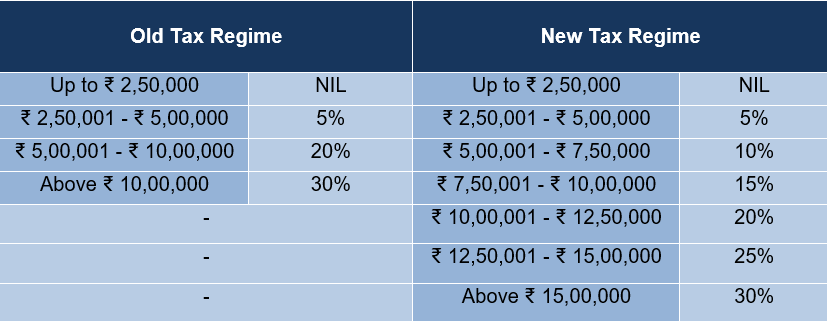
Since, income tax on intraday trading income is calculated based on tax slabs, below are the income slabs for FY 22-23:
What is trading turnover and why does it matter?
Trading turnover is the total value of shares traded in a given period of time.Trading turnover matters because it affects the transaction costs and the price movements of the shares.
Trading Turnover can be calculated either as a scrip-wise or a trade-wise method. Absolute turnover means the sum total of positive and negative differences (the loss amount will not be deducted but added to the profit amount) for the purpose of tax audit calculation as per section 44AB.
Benefits of declaring trading income as speculative business income
You can set off your speculative losses against your speculative gains in the same year or carry forward them for four years.
You can claim deductions for expenses related to your intraday trading activity, such as brokerage, internet charges, software costs, etc.
You can opt for presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD and declare 6% of your turnover as your income if your turnover is less than Rs. 2 crore and you do not maintain books of accounts.
You can avoid tax audit under section 44AB if your turnover is less than Rs. 10 crores and your cash receipts and payments are less than 5% of your total receipts and payments.
How to declare intraday trading income as speculative business income?
To declare your intraday trading income as speculative business income, you need to follow these steps:
Calculate your turnover from intraday trading ie the sale consideration amount and not absolute value of profit and loss from each trade.
Calculate your net profit or loss from intraday trading by deducting expenses from turnover.
Report your net profit or loss from intraday trading under the head "Profits and Gains from business or profession- Speculative Income" in your income tax return.
Pay advance tax on your estimated income from intraday trading every quarter.
Advance Tax Rules for Intraday Traders
Intraday traders are those who buy and sell stocks within the same day. They are liable to pay advance tax if their estimated tax liability for the financial year exceeds Rs. 10,000. Advance tax is to be paid in four instalments during the year (15%, 45%, 75%, 100% of total liability) by those who do not opt for the presumptive taxation.
Presumptive taxation is a scheme that allows intraday traders to declare their income as a percentage of their turnover, without maintaining books of accounts or getting audited. The percentage is 6% for digital transactions and 8% for others.
Intraday traders who opt for presumptive taxation pay advance tax in one single installment, by applying the percentage to their estimated turnover for the year. They can also claim deductions under Chapter VI-A, such as Section 80C, from their presumptive income.
If you need any assistance with filing your income tax return or managing your intraday trading income, you can contact us at JJ Tax. We are a team of experts who can help you with all your taxation and finance needs. We offer personalized and affordable services that suit your requirements.
Thank you for reading our newsletter. We hope you found it informative and useful. Stay tuned for more updates and insights from JJ Tax.
Happy Trading!